Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on for maintenance after it is flooded.
When the motherboard was removed, it was found that many parts of the motherboard under the corresponding keyboard had been corroded by water, which was more serious. There are two new situations, one is that the adapter of the regulated power supply head is not suitable, and the other is that the power-on key of this machine is integrated on the keyboard and cannot be removed, so temporary leads have to be welded on the motherboard.
Machine model: ASUS A541U notebook
Fault phenomenon: the customer described that the notebook stopped turning on after water flooded and needed maintenance.
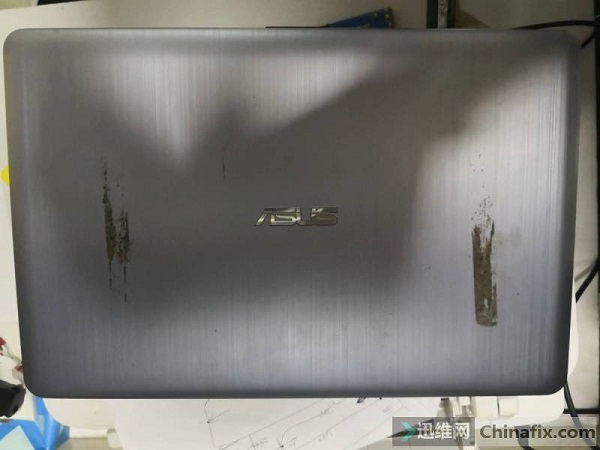

Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 1
Maintenance process:
The manufacturer’s design of this machine is quite interesting. The battery is actually built-in and can’t be taken down in advance, so you need to be extra careful when disassembling the machine to get the motherboard.
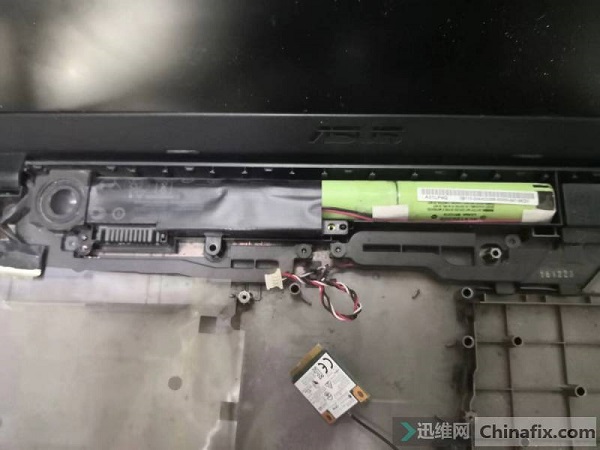

Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 3
When the motherboard was removed, it was found that many parts of the motherboard under the corresponding keyboard had been corroded by water, which was more serious. It doesn’t seem that the water just flooded the day before, as the customer said, but it has been flooded for a long time. There may be no problem and it has never been taken seriously.
After cleaning the motherboard, measure the resistance of each major power supply, and find that there is no short circuit phenomenon, so I decided to power up to see the standby situation. Two new situations were found. First, the switching head of the regulated power supply was not suitable. Second, the power-on key of this machine was integrated on the keyboard and could not be removed, so temporary leads had to be welded on the motherboard.
The lead wire of the power-on key is welded on the filter capacitor corresponding to the cable interface and connected with a switch, which is convenient for power-on test.

Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 6
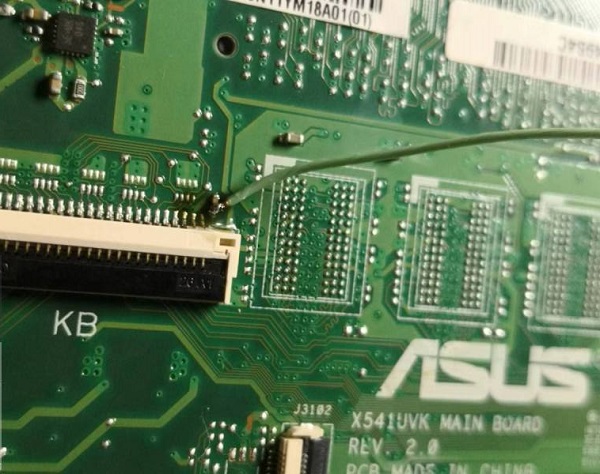

Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 7
The effect after qi huo is as follows:
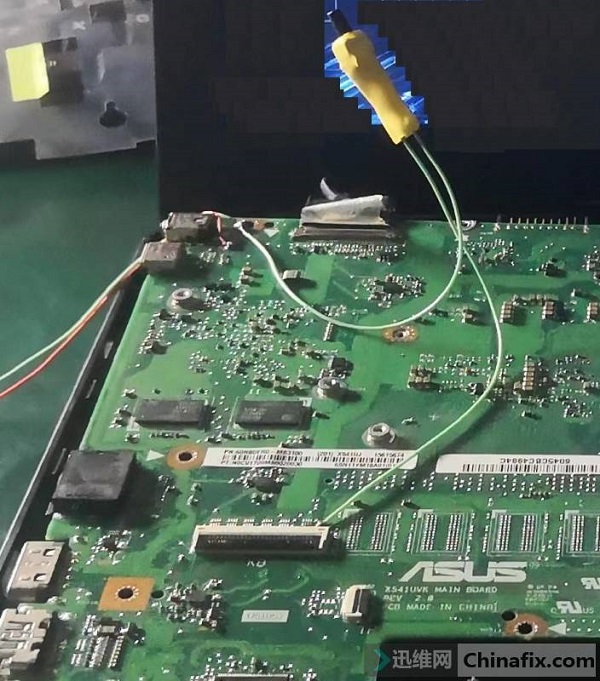

Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 8
After power-on, it is found that the current is stable at 93mA, and there are 3.3V and 5V standby, and the current does not jump when pressing the power-on key. I feel that the current is a little too large when I am on standby. I began to suspect that there is a slight leakage in the back circuit. I pried open the 3.3V inductor and turned it on, and found that the current is stable at about 20mA, so the target tends to be the circuit after 3.3 V. Can check to check, always can’t find a circuit and components with low resistance.
Unintentionally unplugging and unplugging the power supply again, I found that the current was running, as if it were a play. I repeated the test by connecting the display screen, or I could turn on the screen and press the power button to respond. I could turn it on and off, and the standby current was 23mA.
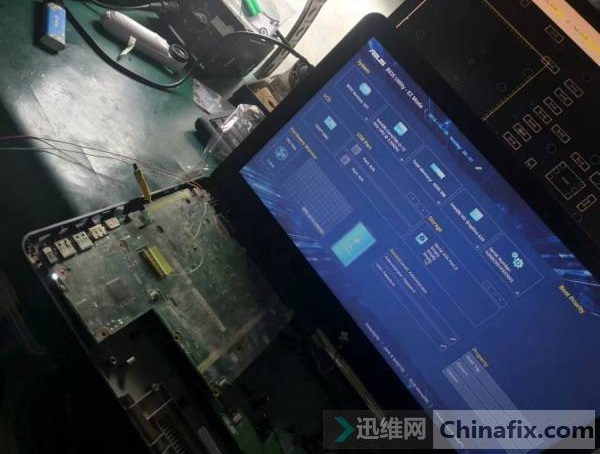

Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 9
Observe the motherboard carefully, and find that the corroded place is not cleaned. Clean the motherboard again, and then power up the test. If it is broken, it will not trigger, and the current will stop at 93mA.
The new discovery is that the current stopped from more than 10 mA to 93mA, so it is seriously suspected that the motherboard triggered, and then stopped at a certain position because of circuit failure, so it is necessary to check the motherboard carefully. Measure the voltage bit by bit against the point bitmap, and finally find an abnormal place.
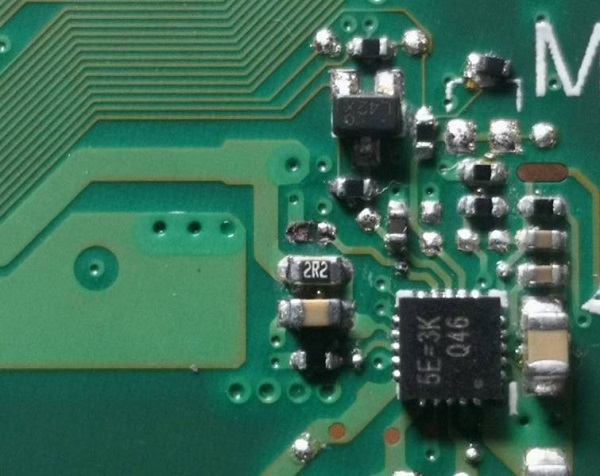
Asus A541U notebook can’t be turned on after water enters. Maintenance Figure 10
The dot bitmap shows a 620K resistor, which is connected to the TCON pin of the memory-powered driver chip nearby. At the beginning of this corrosion, the resistance is still there, and the voltage is sometimes there and sometimes it is not.
Check the drawing resistance directly to B+ on the back through the motherboard via, and B+ in other parts can be measured, but this place is abnormal. After removing the resistor, it was found that the pad had been corroded by a small pit, and the metal sheet at the end of the resistor was gone.
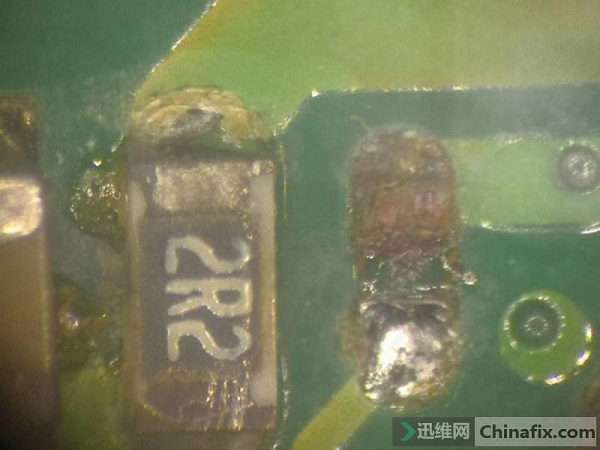

Clean up the place, measure that the exposed copper skin is not short-circuited, fill the pit with green oil, and scrape a tin planting point next to it to prepare for repairing the resistance.
I don’t have a 620K resistor at hand, so I have to check my account on two old desktop motherboards, toss around, find a 400K and a 330K, and string them together for use. Anyway, it’s a current limit, and it should be ok to be a little bigger (in fact, there is no way, there is no same resistance). Fly another wire under the microscope to connect the circuit. The finished product is shown below.
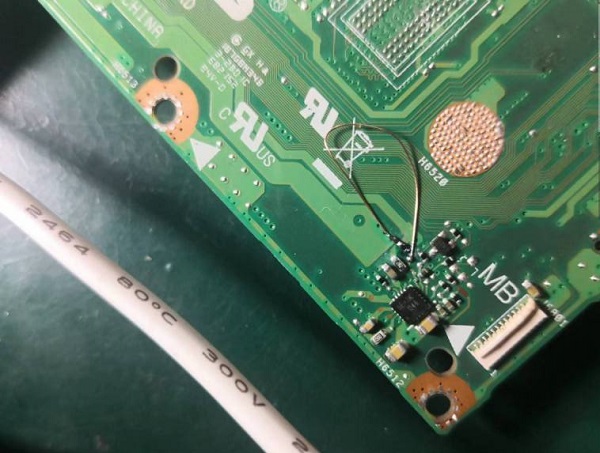

Check that the resistance of each point is normal, there is no short circuit, and fix it with green oil.
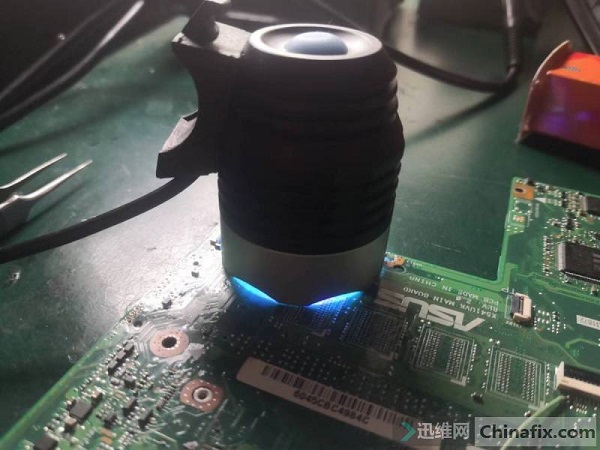

Connect the power supply and observe that the standby current returns to normal, about 23MA. Connect the monitor to start the machine, the current jump is normal, and the machine starts smoothly. Repeated on-off test is no problem, and the installation is finished.
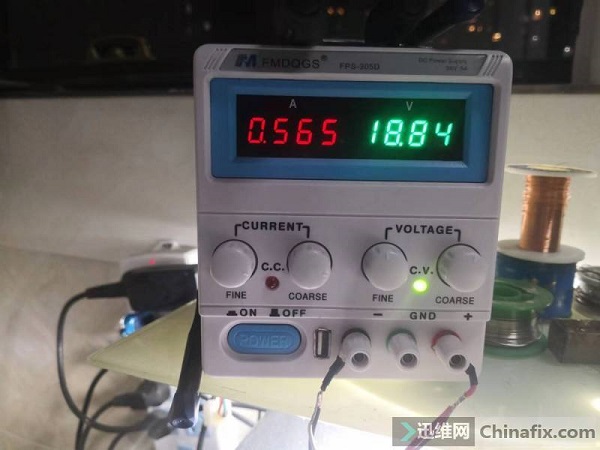

Summary: The current of 93mA at the beginning of power-on commissioning is actually the current after triggering, not the standby current, and their differences should be carefully judged. Secondly, the final failure point of this maintenance is the corrosion part of water inflow, which should have been the focus of attention. If you pay more attention and observe more carefully at the beginning, you should be able to take fewer detours.
